


《高分子化学英文PPT课件下载(红102页)》是由用户上传到老师板报网,本为文库资料,大小为8.54 MB,总共有102页,格式为ppt。授权方式为VIP用户下载,成为老师板报网VIP用户马上下载此课件。文件完整,下载后可编辑修改。
- 文库资料
- 102页
- 8.54 MB
- VIP模板
- ppt
- 数字产品不支持退货
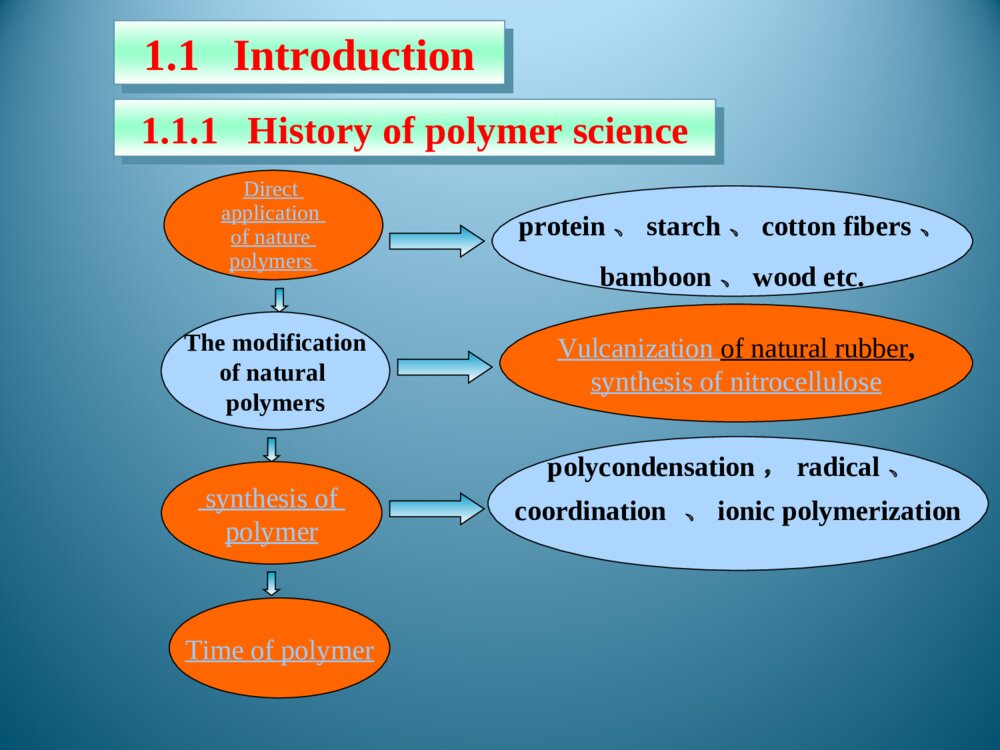
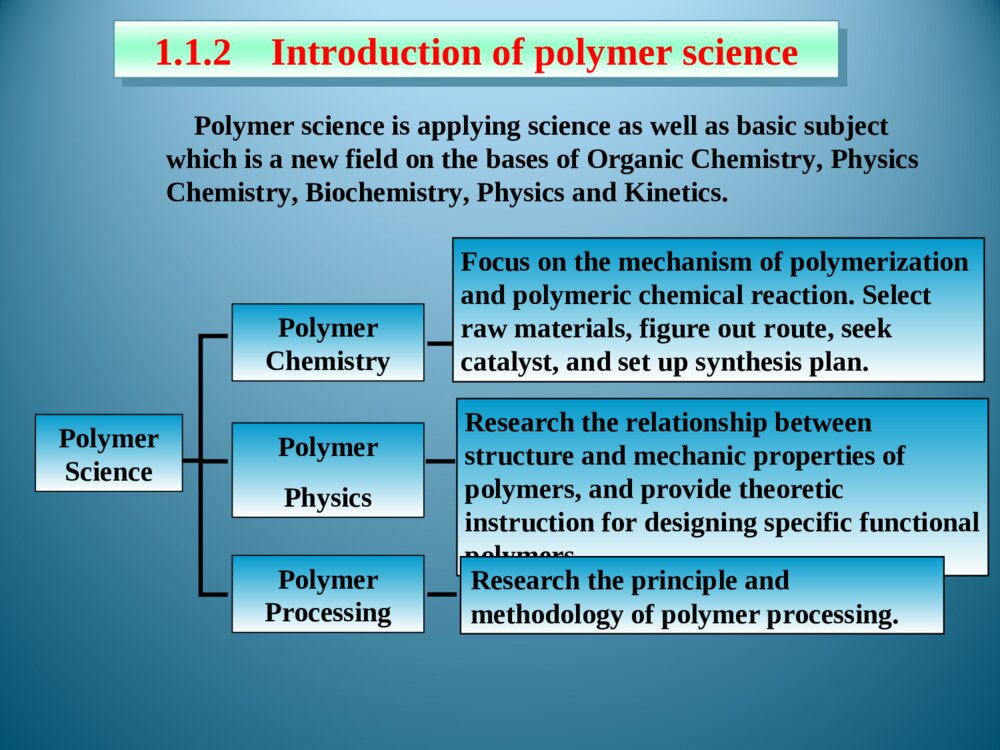
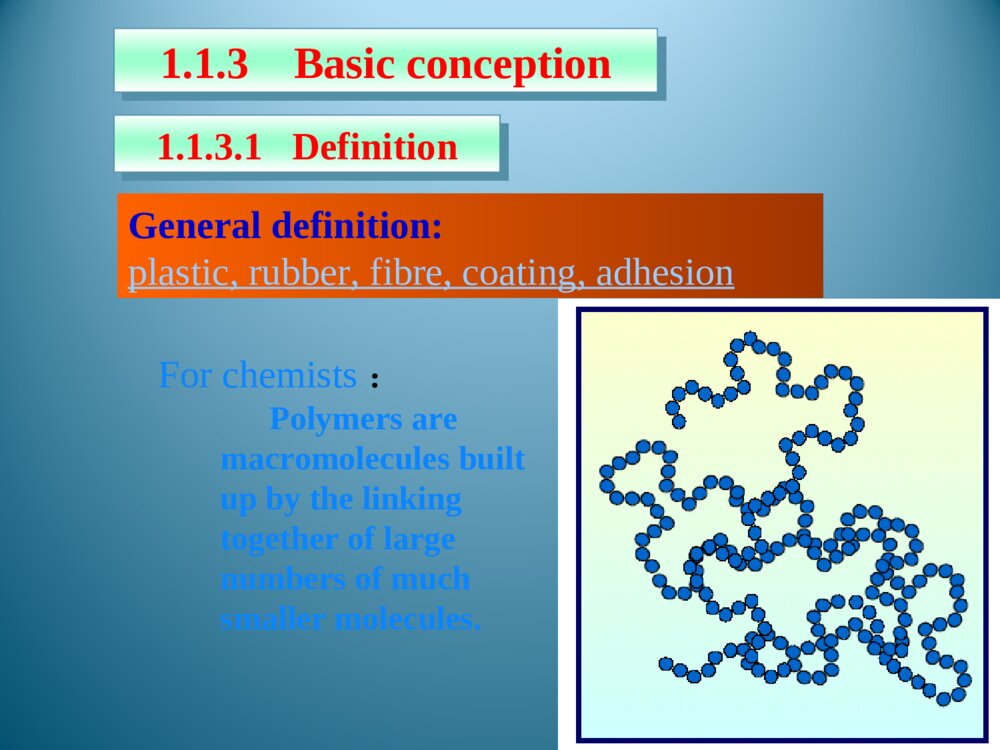
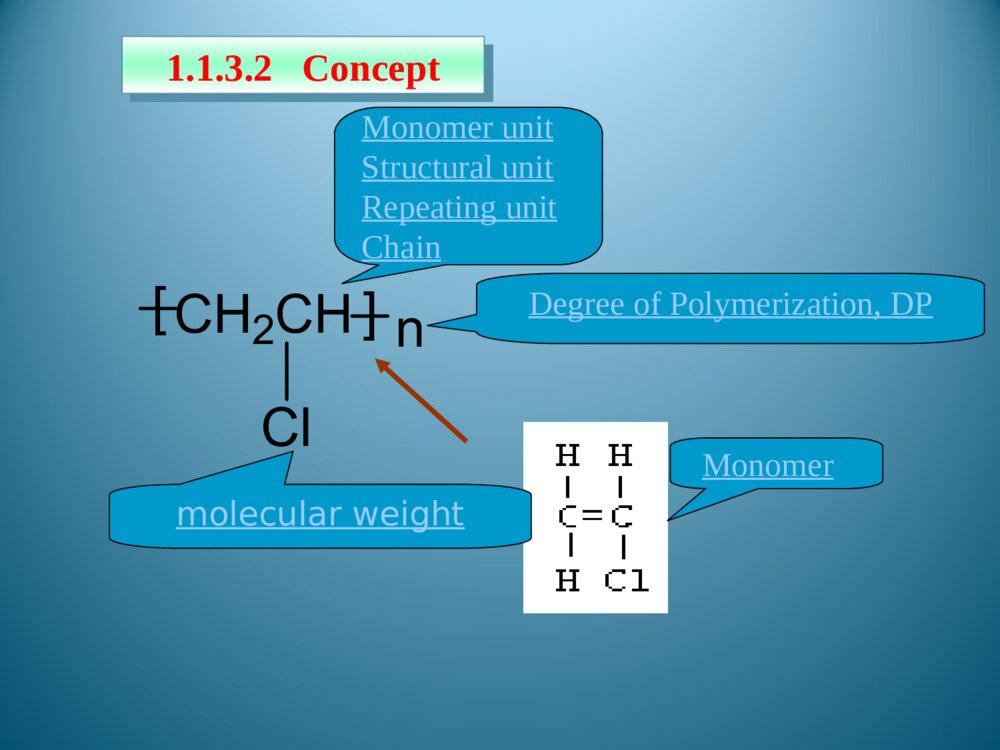
Chapter1Introduction1.1Foreword1.2Typesofpolymersandthenomenclature1.3Polymerization1.5StructureofPolymers1.4MolecularweightanditsdistributionThemodificationofnaturalpolymersDirectapplicationofnaturepolymerssynthesisofpolymerTimeofpolymerprotein、starch、cottonfibers、bamboon、woodetc.Vulcanizationofnaturalrubber,synthesisofnitrocellulosepolycondensation,radical、coordination、ionicpolymerization1.1.1Historyofpolymerscience1.1IntroductionLordToddTheNobelPrizeinChemistry1957Iaminclinedtothinkthatthedevelopmentofpolymerizationisperhapsthebiggestthingthatchemistryhasdone,whereithashadthebiggesteffectoneverydayLife.Introducedtheconceptof“polymer”intoscientificfield,andsetuptheequationbetweentheviscosityofpolymersolutionanditsmoleculeweight.setupthetheoryofpolycondensationcoordinationpolymerizationofethylene、propylene(1963Nobel)Relationsbetweenthemechanicalpropertiesandstructureofpolymers(1974Nobel)Discoveryanddevelopmentofconductivepolymers(2000Nobel)。HermannStaudingerCarothersKarlZiegler,GiulioNattaKarlZiegler,GiulioNattaPaulJ.FloryHidekiShirakawa,AlanG.MacDiarmid,AlanJ.HeegerPolymerSciencePolymerChemistryFocusonthemechanismofpolymerizationandpolymericchemicalreaction.Selectrawmaterials,figureoutroute,seekcatalyst,andsetupsynthesisplan.Researchtherelationshipbetweenstructureandmechanicpropertiesofpolymers,andprovidetheoreticinstructionfordesigningspecificfunctionalpolymers.PolymerPhysicsPolymerProcessingResearchtheprincipleandmethodologyofpolymerprocessing.PolymerscienceisapplyingscienceaswellasbasicsubjectwhichisanewfieldonthebasesofOrganicChemistry,PhysicsChemistry,Biochemistry,PhysicsandKinetics.1.1.2IntroductionofpolymerscienceRestraintsSolutions(1)Elongatethedurableyears(2)Recycle(3)NaturaldegradationEnvironmantalpollutionofpolymericjunkGeneraldefinition:plastic,rubber,fibre,coating,adhesionForchemists:Polymersaremacromoleculesbuiltupbythelinkingtogetheroflargenumbersofmuchsmallermolecules.1.1.3Basicconception1.1.3.1DefinitionCH2CHCl[]nMonomerMonomerunitStructuralunitRepeatingunitChain1.1.3.2ConceptDegreeofPolymerization,DPmolecularweight1.2ClassificationandnomenclatureBasedonuseBasedontheheatingwaymainchainPolymersNomenclatureNon-IUPACIUPACBasedonsourceBasedonstructureTradenamesBasedonmonomer:homopolymerization、copolymerizationBasedonReactingcentre:radicalandionicpolymerization(cationic、anionic)Basedonreaction:linear、open-loop、cyclization、transitioin、isomerizationpolymerizationBasedonElements:additionpolymerization、polycondensationBasedonkinetics:chain、stepsPolymerization:MonomerPolymer1.3PolymerizationFloryPolymerizationBasedonstructuralandcompositionaldifferencesbetweenmonomersandpolymersAdditonpolymerizationPolycondensationBasedonpolymerizationmechanismChainpolymerizationSteppolymerizationCarothers:1.4MolecularweightandMolecularweightDistributionAveragemoleculeweightDistributionMolecularWeightDistribution(MWD)DistributionIndex(HI)Moleculeweightdistributiondiagram(MWD)1.5PolymerstructureOpticalisomerismPolymerstructureMaocromoleculeChainstructureAggregationstructureMacro-structureMicrostructurelinealBranchedCrosslinkedrepeatedunitsSequentialstructureCubicisomerismrotamerismConformationcrystalizationAmor-phousglassyelastomericviscousControlbasicconceptofpolymer。Controlthemechanismofstep,chain,additionpolymerizationandpolycondensation.Understandthenomenclature,classificationofpolymersandtheirmonomersUnderstandthemoleculeweightexpressionandmoleculeweightdistribution。UnderstandtheaggregationofpolymerKeys补充习题1、在聚合反应过程中,分子量随转化率变化规律是,随转化率提高,自由基聚合的分子量,逐步聚合分子量,阴离子聚合的分子量是。2、聚合物是的混合物,其分子量是一平均值,这种分子量的不均一性称做3、尼龙-810是由和缩聚而成的,“8”代表;“10”代表。其反应机理是。4、何谓分子量的多散性?如何a聚合物分子量的多分散性?3KSHermannStaudinger(1881~1965)1920,issuethepaperof“Discussionofpolymerization”1932,editthebookpolymericorganiccompounds1953,NobelPrizeWallace HumeCarothers(1896~1937)1935:InventNylon66GiulioNatta(1903~1979)KarlZiegler(1898~1973)Coordinationpolymerizationofethyleneandpropylene1963Nobelprize,Chem1974Nobelprize:RelationsbetweenthemechanicalpropertiesandstructureofpolymersPaulJ.Flory(1910~1985)ShirakawaHideki(1936~)AlanJ.Heeger(1936~)AlanG.MacDiarmid(1929~)2000NobelPrizeDiscoveryanddevelopmentofconductivepolymersLordToddTheNobelPrizeinChemistry1957Iaminclinedtothinkthatthedevelopmentofpolymerizationisperhapsthebiggestthingthatchemistryhasdone,whereithashadthebiggesteffectoneverydayLife.NaturalPolymers硫化Thefirsttruesyntheticplastic再生真皮(硅橡胶)液晶显示裸鼠背上的人工耳朵(硅橡胶)plasticrubbermonomer:smallmoleculePolymerMonomerCH2CHCl[]nCH2CH[]n[OCH2CH2OOC]OnC--HOCH2CH2OHHOOCCOOHstructuralunitPolymerStructuralUnitCH2CHCl[]nCH2CH[]n[OCH2CH2OOC]OnCrepeatingunitCH2CHCl[]nCH2CH[]n[OCH2CH2OOC]OnC--PolymerRepeatingunitmonomerunitPolymerMonomerunitCH2CHCl[]nCH2CH[]n[OCH2CH2OOC]OnC--?:chainPolymerChainCH2CHCl[]nCH2CH[]n[OCH2CH2OOC]OnC--DegreeofpolymerizationBasedonrepeatingunit:Basedonstructuralunit:DPDPnXnXPolymerDegreeofpolymerization(n)CH2CHCl[]nCH2CH[]nnXDPnnXDPnnXDPn2/MolecularweightM=DPM0OrM=XnM1M0:ThemoleculeorrepeatingunitM1:ThemoleculeofstructuralunitDP:ThenumberofrepeatingunitXn:ThenumberofstructuralunitBasedonusePolymerPlasticRubberCoatingAdhesionFibreCoatingFilmformerPaintSolventAccessoryingredientBasedonheatingwayThermoplasticsExamples:PP,PVC,PS,etc.ThermosetExamples:Phenolicresin,Epoxyresin,Urea-formaldehyderesin.Basedonmainchainstructure1)Carbonchainpolymer:ThemainchainismadeofC.Suchas:PVC,PBD,etc.2)Heterochainpolymer:BesidesC,themainchainismadeofotheratomsasO,NandS.Suchas:polyester,polyether,polyurethane,thiorubber,etc.3)Elementorganicpolymer:ThemainchainisnotmadeofC,it’smadeofSi,B,Al,O,N,Sandsoon.Butthereareorganicgroupsonthesidechain.Suchas:Siliconerubber4)Abio-macromolecule:TherearenoCinthemainchainorsidechain.Suchas:SilicateNaturalrubberPlasticsCurrencyplastics:PVCPSPPPMMAEngineeringplastics:NylonPCCurrencyrubber:naturalrubberSpecialrubber:butyronitrilerubber,siliconerubber,chlorobutadienerubber.butadienestyrenerubbercis1.4polybutadienerubberfiber:cotton,hair,silk,hemp,etc.:Vicosefiber,Cellulosefiber,etc.:terylene、nylon、acrylon、vinylonnaturefiberrayonsyntheticfiberAdhesionNon-IUPAC:easytoremember,butcouldnotexpressthestructural[OCH2CH2]n[OCH2CH2]nCH2CH2O¿ª»·HOCH2CH2OH[OCH2CH2]nÍÑË®ClCH2CHOH[OCH2CH2]nHClClCH2OCH3[OCH2CH2]nHClNon-IUPAC:Polycyclic-ethaneBasedonstructure:PolyoxidizedethyleneAdvantagesanddisadvantagesofnon-IUPACNomenclaturebasedonsourceSuchpolymersarenamedbyaddingthenameofthemonomerontotheprefix“poly”withoutaspaceorhyphen.[CH2CH]OHnCH2CHCl[]nCH2CH[]npolyvinylCloridepolystyrenepolyvinylalcoholResin:phenol+formaldehyde——phenolformaldehyderesinurea+formaldehyde——ureaformaldehyderesinRubber:butadiene+styrene——styrene-butadienerubberbutadiene+vinylcyanide——butadiene-vinylcyanideethylene+propylene——ethylene-propyleneCopolymer:nameofmonomer+“resin”or“rubber”assuffixNomenclaturebasedonstructureThenameofthepolymerisobtainedbyfollowingtheprefixploywithoutaspaceorhyphenwithparenthesesenclosingthenameofthestructuralgroupingattachedtotheparentcompound.—CONH—:polyamide—COO—:polyester—O—:polyether—SO2—:polysulfoneExamples:Anexampleoftrade-namenomenclatureistheuseofthenamenylonforthepolyamidesfromunsubstituted,nonbranchedaliphaticmonomers.TradenamesExamples:nylon6,6poly(hexamethyleneadipamide)nylon6,10poly(hexamethylenesebacamide)Thetradenameofsyntheticfiber,‘fiber’asthesuffixNylonPolyesterVinylonAcrylicPolyvinylchloridefiberPolyproylenefiberNylon-6PETPPVFPANPVCPPThebaseofIUPACpolymernomenclaturesystemistheselectionofapreferredconstitutionalrepeatingunit(abbreviatedasCRU).HereareasummaryofthemostimportantoftheIUPACrulesfornamingsingle-standorganicpolymers.1.2.2.2systematicnomenclaturesystema.ThenameofapolymeristheprefixpolyfollowedinparenthesesorbracketsbythenameoftheCRU.TheCRUisnamedbynamingitssubunits.SubunitsaredefinedasthelargestsubunitsthatcanbenamedbytheIUPACrulesforsmallorganiccompounds.b.TheCRUiswrittenlefttorightbeginningwiththesubunitofhighestseniorityandproceedinginthedirectioninvolvingtheshortestroutetothesubunitnextinseniority.c.Forheteroatomsoracyclicsubunitscontainingheteroatoms,theorderofdecreasingpriorityisO,S,Se,Te,N,P,As,Sb,Bi,Si,Ge,Sn,Pb,B,Hg.Theseniorityofotherheteroatomswithinthisorderisdeterminedfromtheirpositionsintheperiodictable.d.Forcarbocyclicringstheseniorityisaringsystemhavingthegreatestnumberofrings>theringsystemhavingthelargestindividualring>theringsystemhavingthegreatestnumberofatomscommontoitsring.e.Foragivencarbocyclicorheteroclicringsystem:(a)whenringsdifferonlyindegreeofunsaturation,seniorityincreaseswithdegreeofunsaturation;(b)forthesameringsystem,seniorityishigherfortheringsystemhavingthelowestlocationnumber,whichdesignatethefirstpointofdifferenceforringjunctionsf.TheseordersofseniorityaresupersededbytherequirementofminimizingthenumberoffreevalencesintheCRU,thatis,theCRUshouldbebivalentunitwhereverpossible.g.Wherethereisachoicesubunitsshouldbeorientedsothatthelowestlocantresultsforsubstituents•Forexample:-OCH2CH2-Poly(oxydizedethylene)—CH=CHCH2CH2—polybutadienepolyvinylchloridepolystyreneCHCH2ClCHCH2Usefulabbreviation PMMA:polymethylmethacrylateABS:acrylonitrile—butadiene—styreneSBR:styrene-butadienerubber)EPR:ethylene-propylenerubberEVA:ethylene—vinylacetatenCH2=CHClCH2CHCl[]nTheadditionandpolymerizationofalkenemonomers(polymerization)resultant——additionpolymerAdditionpolymerizationReactionofthemulti-stepcondensationandpolymerizationofmonomers,mainresultant——condensationpolymernH2N(CH2)6NH2+nHOOC(CH2)4COOH(2n-1)H2OHOH[NH(CH2)6NHCO(CH2)4CO]n+ReactionbetweenfunctionalgroupspolycondensationQ:Howeversomereactionarehardtobedetermined:(ringopening)CH2CH2O¿ª»·[OCH2CH2]n»·ÑõÒÒÍé¾Û»·ÑõÒÒÍénNH(CH2)5CO[NH(CH2)5CO]n¿ª»·¼º±ûõ£°·ÄáÁú-6HO(CH2)4OHnO=C=N(CH2)6N=C=O+·Ö×Ó¼äÇâתÒÆ£¨¾Û¼Ó³É£©¶¡¶þ´¼¶þÒìÇèËἺõ¥¾Û°±õ¥n[O(CH2)4OCONH(CH2)6NHCO]nCH2N[CH2]nN2+BF3¼ÓÈÈnH3CCH3600¡«1000¡æ[CH2CH2]+nH2neliminaationreaction:chainpolymerizationThedistinguishingcharacteristicofchainpolymerizationisthatpolymergrowthtakesplacebymonomerreactingonlywiththereactivecenter.Monomerdoesnotreactwithmonomerandthedifferent-sizedspeciessuchasdimer,trimer,tetramer,andn-merdonotreactwitheachother.relationbetweentimeandmoleculeweightchainpolymerizationtheconversionincreasesastimepasses,moleculedoesnothaveadramaticchangesteppolymerization——Thecharacteristicofsteppolymerizationthatdistinguishesitfromchainpolymerizationisthatreactionoccursbetweenanyofthedifferent-sizedspeciespresentinthereactionsystem.mostpolycondensationreactionsbelongtostep-mechanismconversion:00MMMCRelationbetweenconversionandtimesteppolymerization:moleculeweightincreasesslowlyasreactiongoesSynthesisofpolyurethane:mechanismofsteppolymerizationwithstructureofcondensationpolymerHO(CH2)4OHnO=C=N(CH2)6N=C=O+·Ö×Ó¼äÇâתÒÆ£¨¾Û¼Ó³É£©¶¡¶þ´¼¶þÒìÇèËἺõ¥¾Û°±õ¥n[O(CH2)4OCONH(CH2)6NHCO]nNH(CH2)5CO[NH(CH2)5CO]n¿ª»·¼º±ûõ£°·ÄáÁú-6Ringopeningreaction:mechanismchangeswithcatalystClassificationofsomepolymnerizationItisveryimportanttoclassifythereactionsaccordingtomechanism,sinceitpointsforwardtheessenceofpolymerizaion.Averagemoleculeweightnumber-averagemolecularweightweight-averagemolecularweightviscosity-averagemolecularweight•commonpolymersnVWMMM•monodispersitynVWZMMMMNumber-averagemolecularweightiiiiiiiinMNNMNNNNMNMNMNM212211N1,N2…Ni:ThenumberofpolymerwhosemoleculeareM1,M2…Mi;Ni:Thepecentofi.Weight-averagemolecularweightiiiiiiiiiiiiiiWMWMNMNMNMNMNMNMNMNWWWMWMWMWM22211222211212211W1,W2…Wi:TheweightofpolymerswhosemoleculeareM1,M2…Mi..Wi:Theweightpecentofi.MeasuringbylightscatteringmethodViscosity-averagemolecularweightMeasuringbyviscosimetry/1/11iiiiiiiVWMWMNMNMα:0.5~0.9HIHI=nMwM/Thelargertheratio,themorewidedistribution.Idealmonodispersepolymer:HI=1Polycondensate(suchaspolyester,polyamide,etc.):TheHIissmaller.Polymers(suchaspolyacrylonitrile,polyvinylchloride,etc.):TheHIislarger.TherangeoftheHIofpolymers:2~50.MWDDistributionofmoleculeweightinatypicalpolymersamplenVWMMMVMWMclosetothemostprobabledistributionnMnearto0.4Linear,branched,andcrosslinkedpolymersPolymerscanbeclassifiedaslinear,branched,orcrosslinkedpolymersdependingontheirstructure.Examples:PEPVCPETPANBranchedBranchedpolymersmoleculesarethoseinwhichtherearesidebranchesoflinkedmonomermoleculesprotrudingfromvariouscentralbranchpointsalongthemainpolymerchain.CrosslinkedWhenpolymersareproducedinwhichthepolymermoleculesarelinkedtoeachotheratpointsotherthantheirends,thepolymersaresaidtobecrosslinked.ThebasicfactortodeterminetheelementsandpropertiesofpolymersRepeatingunitPENylonCH2CHCH4CH2CH2CHOHCH2CHOHCH2CHOHCH2CHOHͷβͷͷββOHOHTheendtowhichattachesthesubstituent——headsequenceofstructuralunitinpolymerchains:•head-totail•headtohead•tailtotailsequentialstructureIsotactic(LLLL)(SSSS)Syndiotactic(SLSL)Random(SLSSLS)antimerisomerismRotamerismofpolyisopreneC=CC=CCH3CH3HHCH2CH2CH2CH2˳ʽ·´Ê½cistransrotamerismarousedbyinternalrotationofmacromoleculechain•spreadingchain•randomcoil•foldedchain•spiralchainconformationA—glassystate;B—highelasticstate;C—viscousstate•glassystate•highelasticstate•viscousstatePhysicandmechanicstateofamorphouspolymer•Tg——temperaturewhentransitionfromglassystatetohighelasticstatehappens•Tf——temperaturewhentransitionfromtohighelasticstatetoviscousstatehappensheattransitiontemperatureMeltingpointTm:temperaturewhenphasetransitionhappensTg—Highestusingtemperatureofamorphousplastic,50~75abovetheroomtemperature℃lowestusingtemperatureofrubber,75belowthe℃roomtemperatureTm—thehighestusingtemperatureofcrystallizedplasticplastic:highTg,aboveroomtemperature、rubber:lowTg、belowroomtemperaturefiber:highTm



















